What would a world without vaccines even look like?
Well, it turns out that we do not have to wonder since accurate historical records allow us to distinctly see and learn for ourselves. This is in keeping with our Secretary of Health and Human Services’ (HHS) recent guidance to Do Your Own Research.
What we actually need, individually and as a nation, is clear and consistent science-based advice when it comes to our health care decisions. That information is best obtained individually through a trusting partnership-type relationship with a scientifically trained, experienced personal physician, and nationally by way of fully trained and career-committed public health experts.
However, “doing our own research” without having highly developed critical thinking experience and skills puts us all at risk of the cognitive error of confirmation bias; that is, abandoning our research efforts as soon as we encounter a source which agrees with our preconceived notion of what we think should be true. As Tom Nichols aptly put it in “The Death of Expertise“: “Having equal rights does not mean having equal talents, equal abilities, or equal knowledge. It assuredly does not mean that ‘everyone’s opinion about anything is as good as anyone else’s.’ And yet, this is now enshrined as the credo of a fair number of people despite being obvious nonsense.”
Our current HHS Secretary appears to be a well-educated, reasonably intelligent, and articulate individual, but he has not convincingly demonstrated an avoidance of bias or any significant respect for the greater expertise of more fully trained and experienced health care professionals who do not share his biases. So, it is alarming but not necessarily surprising that he is all over the map on his statements regarding the benefits of vaccination, having made each of the following statements:
- “If you want to avoid spreading measles, the best thing you can do is take that vaccine.”
- “All of my kids are vaccinated.”
- “What would I do if I could go back in time and I could avoid giving my children the vaccines that I gave them? I would do anything for that. I would pay anything to be able to do that.“
- “Anti-vax physicians had treated and healed some 300 measles-stricken Mennonite children”… by using “aerosolized budesonide and clarithromycin” to treat children with measles.”
- “No vaccine is safe or effective.“
As it turns out regarding item #4, neither the steroid budesonide nor the antibiotic clarithromycin have any direct effects on healing the body from the measles virus infection. I will stop here, though I could go on about misinformation coming from the highest level of federal health care guidance. The Secretary has apparently taken to heart his boss’s guidance to Go Wild on Health Care!
So, here are just three examples of what that world without vaccines would actually look like:
Smallpox
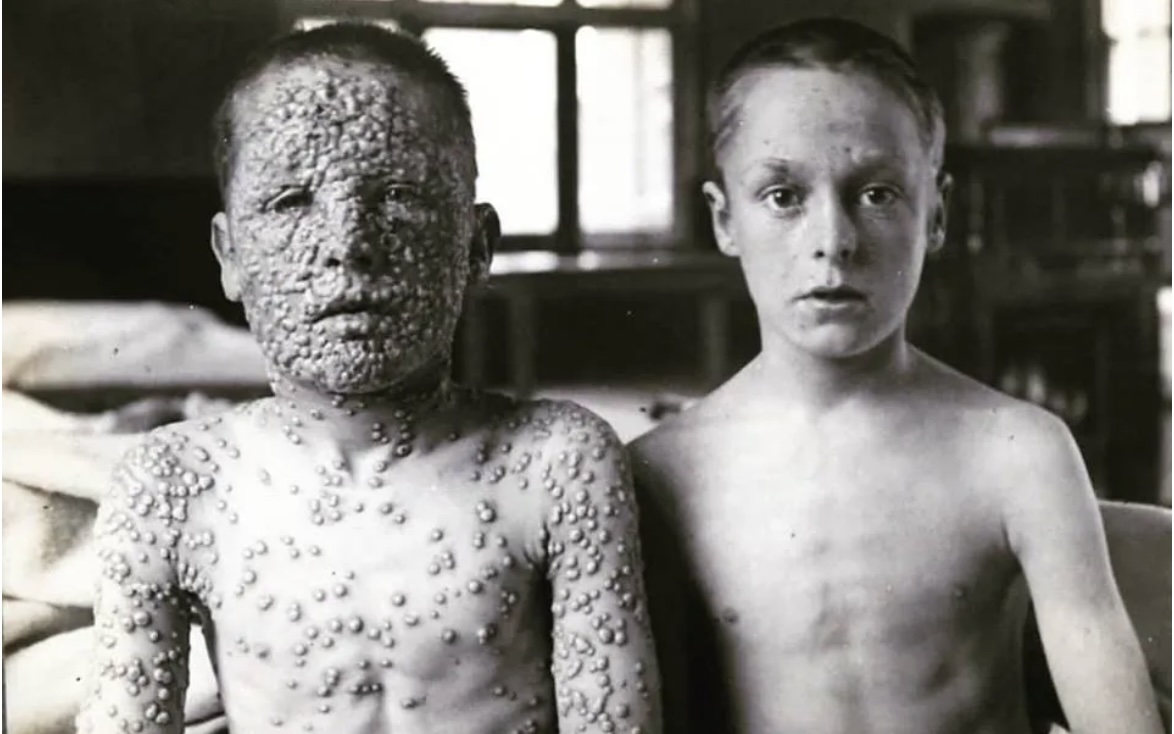
An estimated 300 million people died from smallpox in the 20th century alone. This virulent disease, which kills a third of those it infects, is known to have co-existed with human beings for thousands of years. As the world’s population grew and travel increased, so the virus that Edward Jenner called the “speckled monster” grasped every opportunity to colonize the world.
Fortunately for all of us, smallpox vaccination is the poster child of vaccination success. The World Health Organization’s sustained, concerted effort has completely eradicated wild smallpox virus from the face of the planet. The last naturally occurring case of smallpox was identified in Somalia in 1977. Out of an abundance of caution, the WHO waited three more years before announcing the successful eradication of smallpox. I happened at the time to be in my fourth/final year of medical school when I heard that news. I still recall that my reaction was, “Wait, wait, what? No wild poliovirus particles out of the countless billions are still alive anywhere on the planet?” (Some samples were preserved in research facilities in the U.S. and USSR). My reaction also was that this represented perfect health equity. This meant that everyone now had the exact same 0 percent risk of contracting a wild smallpox virus infection, regardless of one’s position in life, degree of power, wealth, influence, etc. In the United States, routine vaccination had already been discontinued in 1971, after the last major U.S. smallpox outbreak in 1949; thus eliminating any further costs of smallpox vaccination programs or risks of vaccine side effects. Having been born in 1953, I still have a faintly visible smallpox vaccination depressed scar on my left shoulder.
Poliomyelitis
I also benefitted from receiving the polio vaccine shortly after its introduction in 1953, after Dr. Jonas Salk had first tested it on himself and his own family and then had run a large study (1.9 million children) proving its safety and effectiveness. “The results were announced on 12 April 1955, and Salk’s inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) was licensed on the same day. By 1957, annual cases dropped from 58,000 to 5,600, and by 1961, only 161 cases remained,” in the U.S.
I was subsequently extremely fortunate and grateful for the opportunity to volunteer with the combined CDC/WHO’s polio eradication efforts for several month stretches in Pakistan in 2000 and then again in Ghana in 2002. In Pakistan, we encountered misinformation unique to that country’s culture. It was a not uncommon belief, fostered by the regional Muslim clergy, as well as by some local physicians, that the oral polio vaccine was a surreptitious way that the western nations would cause infertility to occur later in life amongst the female Muslim children who received it. On the progress side, as a result of the global polio eradication initiative, “Wild poliovirus cases have decreased by over 99 percent since 1988, from an estimated 350,000 cases in more than 125 endemic countries to 12 reported cases in 2023 … in just the two countries of Pakistan and Afghanistan.”
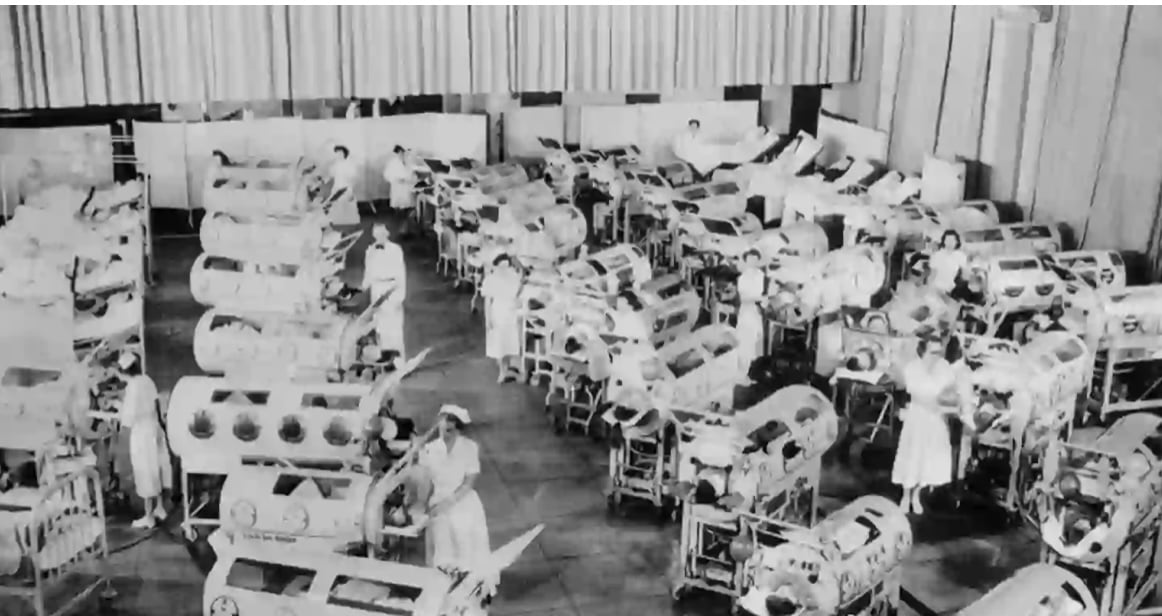
Iron-lung ward at Rancho Los Amigos Hospital, Downey (Los Angeles County), California, c1953. (Contributed by Dr. Douglas Lanska. Courtesy of the Rancho Los Amigos National Rehabilitation Center (Rancho Los Amigos) in Downey, California. Used with permission.)
Measles
“Due to the ease with which measles is transmitted from person to person in a community, more than 95 percent of the community must be vaccinated in order to achieve herd immunity. Vaccination resulted in an 80 percent decrease in deaths from measles between 2000 and 2017, with about 85 percent of children worldwide having received their first dose as of 2017. Measles affects about 20 million people a year, primarily in the developing areas of Africa and Asia. It is one of the leading vaccine-preventable disease causes of death. In 1980, 2.6 million people died from measles, and in 1990, 545,000 died due to the disease; by 2014, global vaccination programs had reduced the number of deaths from measles to 73,000. Despite these trends, rates of disease and deaths increased from 2017 to 2019 due to a decrease in immunization.”
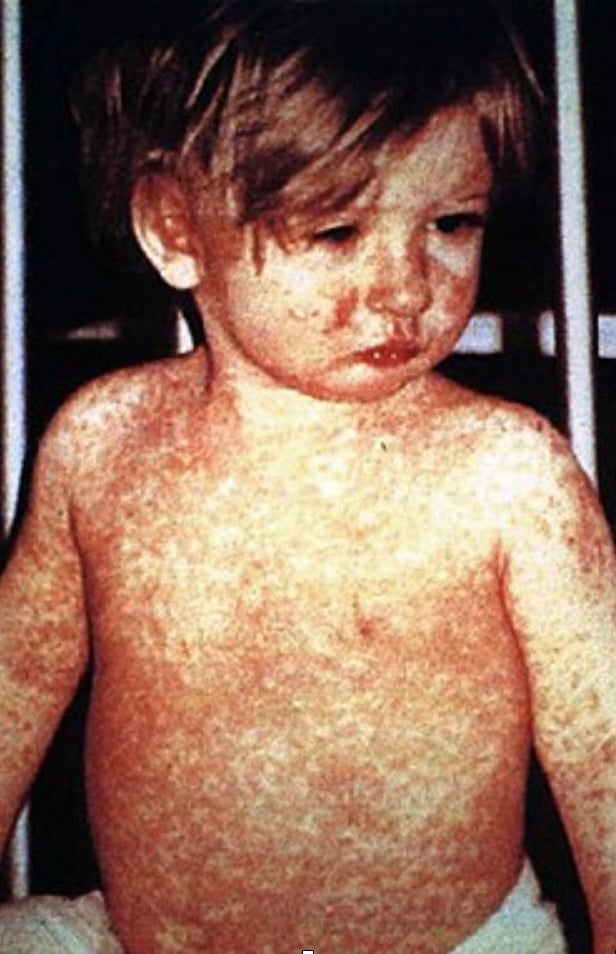
The MMR vaccine was introduced in 1971, resulting in measles being eliminated in the U.S. by 2000. Routine transmission among U.S. children was eliminated but not totally eradicated, since unvaccinated populations remained susceptible and infected travelers could therefore reintroduce the virus, as is happening right now in the western Texas region and beyond. In my own case, my mother informed me that as an infant I had become worryingly ill with a case of measles, losing substantial weight, but fortunately dodging the more serious complications of pneumonia and/or encephalitis. There have been repeated expert reviews debunking the theory that the MMR vaccine causes autism; medical professionals consider it “settled science” that there is no causal relationship. One more fact that I did not include there is that fully ten of that study’s original thirteen authors subsequently chose to retract that interpretation of their findings.
We remain on the verge of duplicating the smallpox success by complete worldwide eradication of poliovirus infections. A similar success with measles disease is also theoretically possible. However, given the United States’ inarguable advantages of greater public literacy rates, a stable democratic government and an enviably modernized health care system, it is ironic that we are currently facing greater challenges of disease control and possible eradication as a result of incompletely informed anti-vaccination sentiments in the western world. Unsurprisingly, measles and polio cases are rising steadily as vaccinations fall, along with other previously common but proven vaccine-controllable childhood infectious diseases.
Drew Remignanti is an emergency physician.
























![AI censorship threatens the lifeline of caregiver support [PODCAST]](https://kevinmd.com/wp-content/uploads/Design-2-190x100.jpg)
